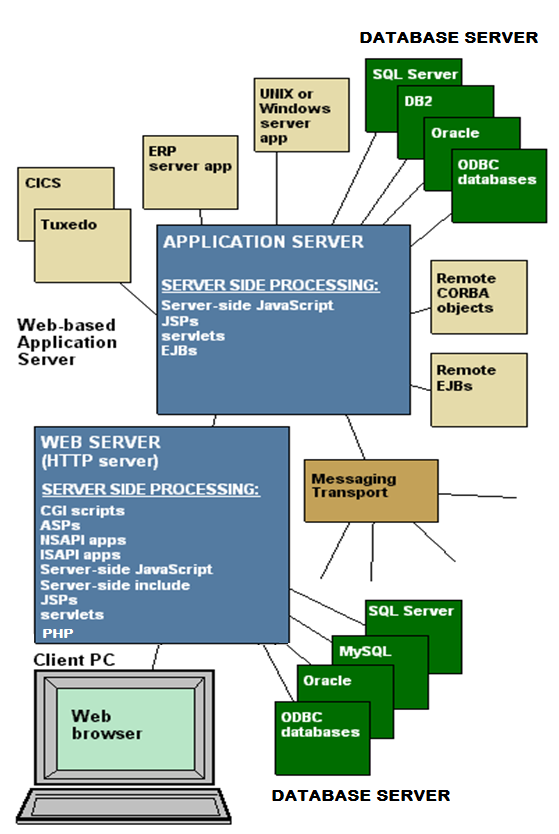
CREATING DYNAMIC WEB PAGES
Server-side Programming
CGI
The traditional way of adding functionality to a Web Server is the Common Gateway
Interface (CGI), a language-independent interface that allows a server to start an
external process which gets information about a request through environment variables,
the command line and its standard input stream and writes response data to its standard output stream.
CGI programs are usually written in interpreted languages like Perl).
NSAPI
Netscape Server API, an API for Netscape's Web servers. NSAPI enables programmers
to create Web-based applications that are more sophisticated and run much faster
than applications based on CGI scripts.
ISAPI
The Internet Server Application Programming Interface (ISAPI) is an N-tier API of
Internet Information Services (IIS), Microsoft's collection of Windows-based web
server services. The most prominent application of IIS and ISAPI is Microsoft's web server.
Servlets
Servlets are modules of Java code that run in a server application (hence the
name "Servlets", similar to "Applets" on the client side) to answer client requests.
Servlets are not tied to a specific client-server protocol but they are most commonly
used with HTTP and the word "Servlet" is often used in the meaning of "HTTP Servlet".
ASP
Active Server Pages (ASPs) are a server side scripting technology made by Microsoft and it use Visual Basic language.
It works on Microsoft IIS server
JSP
Java Server Pages was developed by Sun. It uses Java language as the scripting language.
JSPs can connect to any database system simply by loading the driver for the database, then connect.
JavaScript
JavaScript was developed by Netscape, Inc., and is not part of the Java platform.
JavaScript, does not create applets or stand-alone applications. JavaScript resides inside HTML documents,
and can provide levels of interactivity to web pages that are not achievable with simple HTML.
SSI
SSI (Server Side Includes) are directives that are placed in HTML pages, and evaluated on the server
while the pages are being served. They let you add dynamically generated content to an existing HTML page,
without having to serve the entire page via a CGI program, or other dynamic technology.
EJB
Enterprise JavaBeans (EJB) technology is the server-side component architecture for Java Platform,
Enterprise Edition (Java EE). EJB technology enables rapid and simplified development of distributed,
transactional, secure and portable applications based on Java technology.
PHP
PHP is a robust, server-side, open source scripting language that is
extremely flexible and actually fun to learn. PHP is also cross platform,
which means your PHP scripts will run on a UNIX®, Linux®, or Windows® server.
Web Servers
IIS
IIS Windows Web Server has been developed by the software giant, Microsoft.
It offers higher levels of performance and security than its predecessors.
It also comes with a good support from the company and is the second most
popular server on the web.
Apache Web Server
Free and the most popular web server in the world developed by the Apache Software Foundation.
Apache web server is an open source software and can be installed and made to work on almost
all operating systems including Linux, Unix, Windows, FreeBSD, Mac OS X and more.
About 60% of the web server machines run the Apache web server
Apache Tomcat
The Apache Tomcat has been developed to support servlets and JSP scripts.
Though it can serve as a standalone server, Tomcat is generally used along
with the popular Apache HTTP web server or any other web server.
Apache Tomcat is free and open source and can run on different operating
systems like Linux, Unix, Windows, Mac OS X, Free BSD.
Zeus Web Server
The Zeus web server runs on Linux and Free BSD operating systems among others.
It has been developed by Zeus technology Ltd. And is known for its speed,
reliability, security and flexibility. The web server is used on some of the
busiest web sites of the world including Ebay. Zeus web server is not free
and costs more than a thousand pounds.
Abyss Web Server
Abyss compact web server runs on all popular platforms - Windows, Mac OS X, Linux
and FreeBSD. The personal edition is (X1) 100% free while the professional Abyss
Web Server X2 has a small price tag of $60. Supports HTTP/1.1, secure connections,
CGI/FastCGI, custom error pages, password protection and much more. The server also
has an automatic antihacking system and a multiligual remote web management interface.
Nginx Web Server
Free open source popular web server including IMAP/POP3 proxy server. Hosting about 7.5%
of all domains worldwide, Nginx is known for its high performance, stability, simple
configuration and low resource usage. This web server doesn't use threads to handle
requests rather a much more scalable event-driven architecture which uses small and
predictable amounts of memory under load.
Jigsaw Web Server
Jigsaw (W3C's Server) comes from the World Wide Web Consortium. It is open source and
free and can run on various platforms like Linux, Unix, Windows, Mac OS X Free BSD etc.
Jigsaw has been written in Java and can run CGI scripts and PHP programs.
Web Databases
MySQL
SQL is the standard query language for interacting with databases. MySQL is
an open source, SQL database server that is more or less free and extremely
fast. MySQL is also cross platform.
SQL Server
Microsoft SQL Server is a computer application used to create desktop, enterprise, and web-based database applications.
Oracle
Introduced in the late 1970s, Oracle was the first database product to run on a variety of platforms from micro to mainframe.
It has a JVM (Java interpreter) built into the DBMS. Thus, triggers and stored procedures can be written and executed in Java
rather than Oracle's PL/SQL programming language.
DB2
DB2 is produced by IBM. DB2 databases can be accessed from any application program by using Microsoft's Open Database Connectivity (ODBC) interface,
the Java Database Connectivity (JDBC) interface, or a CORBA interface broker.
Using PHP
A normal HTML website will not pass data from one page to another. In other words, all information is forgotten when a new page is loaded. This makes it quite a problem for tasks like a shopping cart, which requires data(the user's selected product) to be remembered from one page to the next.
PHP Sessions - Overview
A PHP session solves this problem by allowing you to store user information on the server for later use (i.e. username, shopping cart items, etc). However, this session information is temporary and is usually deleted very quickly after the user has left the website that uses sessions.
It is important to ponder if the sessions' temporary storage is applicable to your website. If you require a more permanent storage you will need to find another solution, like a MySQL database.
Sessions work by creating a unique identification(UID) number for each visitor and storing variables based on this ID. This helps to prevent two users' data from getting confused with one another when visiting the same webpage.
Note:If you are not experienced with session programming it is not recommended that you use sessions on a website that requires high-security, as there are security holes that take some advanced techniques to plug.
Starting a PHP Session
Before you can begin storing user information in your PHP session, you must first start the session. When you start a session, it must be at the very beginning of your code, before any HTML or text is sent.
Below is a simple script that you should place at the beginning of your PHP code to start up a PHP session.
PHP Code:
<?php session_start(); // start up your PHP session! ?>
This tiny piece of code will register the user's session with the server, allow you to start saving user information and assign a UID (unique identification number) for that user's session.
Storing a Session Variable
When you want to store user data in a session use the $_SESSION associative array. This is where you both store and retrieve session data. In previous versions of PHP there were other ways to perform this store operation, but it has been updated and this is the correct way to do it.
PHP Code:
<?php session_start(); $_SESSION['views'] = 1; // store session data echo "Pageviews = ". $_SESSION['views']; //retrieve data ?>
Display:
In this example we learned how to store a variable to the session associative array $_SESSION and also how to retrieve data from that same array.
PHP Sessions: Using PHP's isset Function
Now that you are able to store and retrieve data from the $_SESSION array, we can explore some of the real functionality of sessions. When you create a variable and store it in a session, you probably want to use it in the future. However, before you use a session variable it is necessary that you check to see if it exists already!
This is where PHP's isset function comes in handy. isset is a function that takes any variable you want to use and checks to see if it has been set. That is, it has already been assigned a value.
With our previous example, we can create a very simple pageview counter by using isset to check if the pageview variable has already been created. If it has we can increment our counter. If it doesn't exist we can create a pageview counter and set it to one. Here is the code to get this job done:
PHP Code:
<?php
session_start();
if(isset($_SESSION['views']))
$_SESSION['views'] = $_SESSION['views']+ 1;
else
$_SESSION['views'] = 1;
echo "views = ". $_SESSION['views'];
?>
The first time you run this script on a freshly opened browser the if statement will fail because no session variable views would have been stored yet. However, if you were to refresh the page the if statement would be true and the counter would increment by one. Each time you reran this script you would see an increase in view by one.
Cleaning and Destroying your Session
Although a session's data is temporary and does not require that you explicitly clean after yourself, you may wish to delete some data for your various tasks.
Imagine that you were running an online business and a user used your website to buy your goods. The user has just completed a transaction on your website and you now want to remove everything from their shopping cart.
PHP Code:
<?php
session_start();
if(isset($_SESSION['cart']))
unset($_SESSION['cart']);
?>
You can also completely destroy the session entirely by calling the session_destroy function.
PHP Code:
<?php session_start(); session_destroy(); ?>
Destroy will reset your session, so don't call that function unless you are entirely comfortable losing all your stored session data!